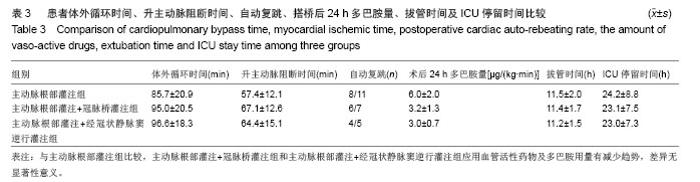
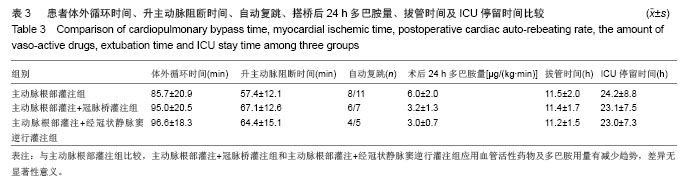
| [1]Chaudhry UA,Harling L,Rao C,et al.Off-pump versus on-pump coronary revascularization: meta-analysis of mid- and long-term outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;98(2):563-572.
[2]Khan MS, Islam MY, Ahmed MU, et al. On pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery versus off pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a review. Glob J Health Sci. 2014;24;6(3):186-193.
[3]Bolourian AA, Foroughi M, Beheshty M, et al. Results of on-pump versus off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90(1):358-359.
[4]Menasché P. Strategies to improve myocardial protection during extracorporeal circulation. Shock. 2001;16 Suppl 1: 20-23.
[5]Jeysen ZY, Gerard L, Levant G, et al. Research report: the effects of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning on myocardial biomarkers of cardioprotection in patients having coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2011; 38(3):175-185.
[6]Hausenloy DJ, Boston-Griffiths E, Yellon DM. Cardioprotection during cardiac surgery. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;94(2):253-265.
[7]Bezon E,Choplain JN, Khalifa AA, et al. Continuous retrograde blood cardioplegia ensures prolonged aortic cross-clamping time without increasing the operative risk. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2006;5(4):403-407.
[8]Frank A, Bonney M, Bonney S, et al. Myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: from basic science to clinical bedside. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2012;16(3):123-132.
[9]Zweier JL, Talukder MA. The role of oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2006 May 1;70(2):181-190.
[10]Kevin LG, Novalija E, Stowe DF. Reactive oxygen species as mediators of cardiac injury and protection: the relevance to anesthesia practice. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(5):1275-1287.
[11]Hu Z, Yan Z, Wang H, et al. Comparative analysis of preservation method and intermittent perfusion volume on the expression of endothelial and inflammatory markers by coronal artery and myocardium in porcine donor hearts. ASAIO J. 2014;60(6):681-687.
[12]Symons JA, Myles PS. Myocardial protection with volatile anaesthetic agents during coronary artery bypass surgery: a meta-analysis.Br J Anaesth. 2006;97(2):127-136.
[13]Keshavamurthy S,Blackstone EH,Pettersson GB.Comment on: Retrograde cardioplegia revisited: open technique for long aortic cross clamping. Heart Lung Circ. 2014;23(6):589.
[14]Yavuz S, Kasap M, Parlar H, ET AL. Heat shock proteins and myocardial protection during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Int Med Res. 2011;39(2):499-507.
[15]Kouerinis IA, Manopoulos CG, Zografos GC, et al. Retrograde cardioplegia in CABG: is it really useful? The microcirculation and a capillary unit model. Med Sci Monit. 2006;12(11): RA265-8.
[16]Onorati F, Santarpino G,Cristodoro L,et al.Continuous coronary sinus perfusion reverses ongoing myocardial damage in acute ischemia. Artif Organs. 2009;33(10): 788-797.
[17]Velissaris T, Khan OA, Asopa S, et al. Myocardial protection during reoperative cardiac surgery: early experience with a new technique.Tex Heart Inst J. 2010;37(1):75-78.
[18]Tiwari RP, Jain A, Khan Z, et al. Cardiac troponins I and T: molecular markers for early diagnosis, prognosis, and accurate triaging of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Mol Diagn Ther. 2012;16(6):371-381.
[19]Emkanjoo Z, Mottadayen M, Givtaj N, et al. Evaluation of post-radiofrequency myocardial injury by measuring cardiac troponin I levels. Int J Cardiol. 2007;25;117(2):173-177.
[20]Vikenes K, Melberg T, Farstad M, et al. Long-term prognostic value of CK-MB and the troponins after angioplasty in patients with stable angina. Scand Cardiovasc J.2011;45(3):146-152.
[21]Ruengsakulrach P,Buxton BF.Anatomic and hemodynamic considerations influencing the efficiency of retrograde cardioplegia. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71(4):1389-1395.
[22]Kinoshita T, Asai T. Preservation of myocardium during coronary artery bypass surgery. Curr Cardiol Rep.2012; 14(4):418-423.
[23]Fazel S,Borger MA,Weisel RD,et al.Myocardial protection in reoperative coronary artery bypass grafting. J Card Surg. 2004; 19(4):291-295. |